New Additions to the Scientific Database
Mar 23, 2016
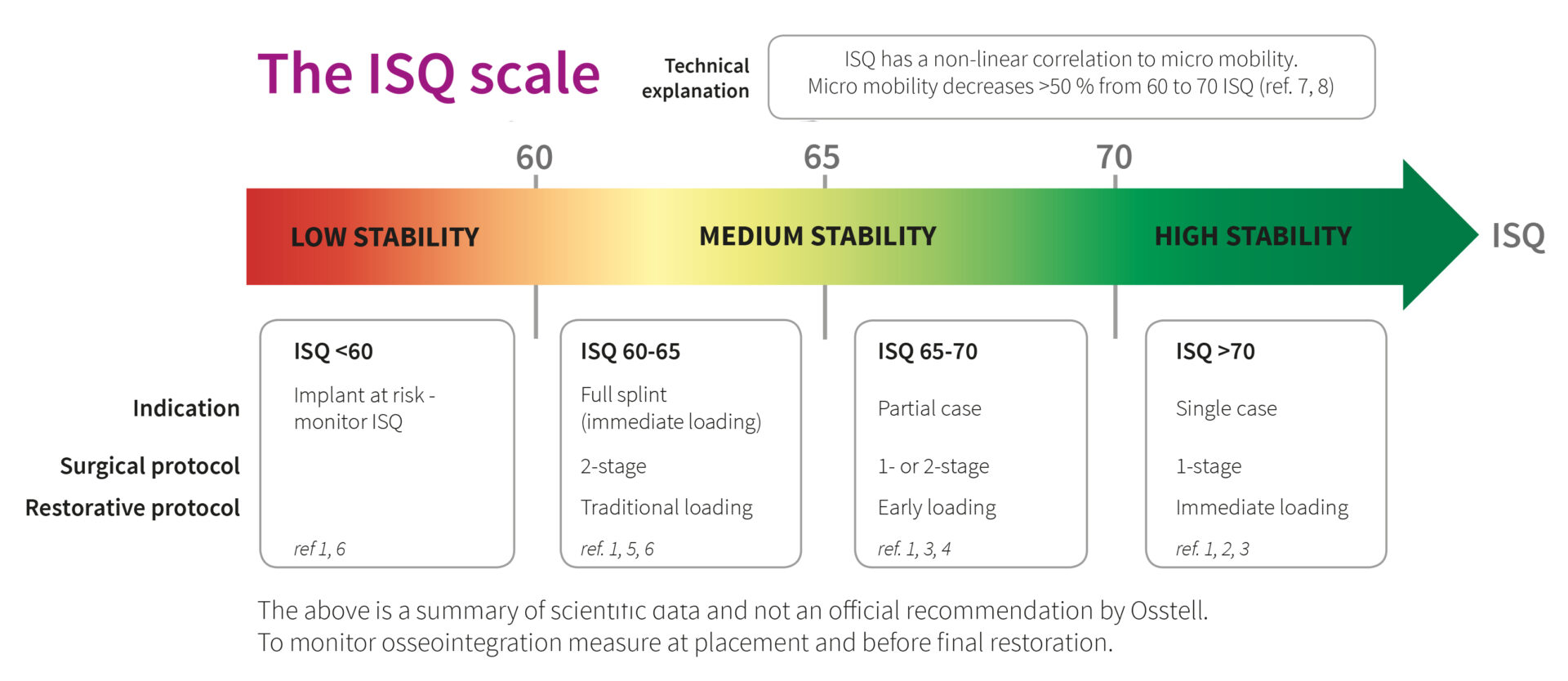
Our regularly updated database now includes close to 860 articles relating to Osstell.
Development of Implant Stability Quotient values of implants placed with simultaneous sinus floor elevation – results of a prospective study with 109 implants
Kuchler U, Chappuis V, Bornstein MM, Siewczyk M, Gruber R, Maestre L, Buser D.
Clin Oral Implants Res. 2016 Jan 16. doi: 10.1111/clr.12768
OBJECTIVES:
In patients with implant placement and simultaneous sinus floor elevation (SFE), healing periods of 6 months have been the standard of care for more than 25 years. The primary objective of this prospective case series study was to determine what percentage of implants placed with SFE reach a threshold Implant Stability Quotient (ISQ) of ≥70 after 8 weeks of healing using Resonance Frequency Analysis (RFA).
CONCLUSIONS:
This study showed that 83% of implants reached the threshold level of ISQ ≥ 70 after 8 weeks, allowing an early loading protocol. The early failure rate was considered low with 0.9%. The RFA technology is a suitable method to objectively monitor implant stability longitudinally.
Early loading of titanium dental implants with an intra-operatively conditioned hydrophilic implant surface after 21 days of healing
Hicklin SP, Schneebeli E, Chappuis V, Janner SF, Buser D, Brägger U.
Clin Oral Implants Res. 2015 Dec 23. doi: 10.1111/clr.12706
OBJECTIVES:
The aim of the present observational medical device performance study was to test whether implants with an intra-operatively conditioned hydrophilic surface can be safely reconstructed when applying an early loading protocol after 21 days in partially edentulous posterior mandibles.
CONCLUSION:
Functional occlusal loading of implants with a hydrophilic, moderately rough endosseal surface 3 weeks after placement appears to be a safe and predictable treatment option in healed sites in the posterior mandible without need of bone augmentation procedures.
Comparative study of immediate functional loading and immediate non-functional loading of monocortical implants
Singh JP, Gupta AK, Dhiman RK, Roy Chowdhury SK
Med J Armed Forces India. 2015 Dec;71(Suppl 2):S333-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mjafi.2013.11.009
BACKGROUND:
Attempts to shorten the overall length of treatment have focused on immediate loading, subsequent to implant placement. Prosthetic rehabilitation immediately after implant placement can be either functional or non-functional in nature. There is paucity of literature on the comparative evaluation of immediate functional and immediate non-functional loading of implants. This in-vivo study was undertaken to comparatively evaluate Immediate Functional Loading and Immediate Non-Functional Loading of monocortical implants with a follow-up period of 18 months.
CONCLUSION:
Both the IFL and INFL protocols can be undertaken satisfactorily in rehabilitation using endosseous implants; however, the main factors for success in IFL and INFL are case selection, meticulous treatment planning and the precision of technique.
Effect of implant macro-design on primary stability: A prospective clinical study
Lozano-Carrascal N, Salomó-Coll O, Gilabert-Cerdà M, Farré-Pagés N, Gargallo-Albiol J, Hernández-Alfaro F
Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2016 Jan 31:0
BACKGROUND:
Implant restorations have become a high predictable treatment option. Several caracteristics such as surgical technique andimplant design can influence the treatment outcomes. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the influence of implant macro-design on primary stability measured with resonance frequency analysis (RFA) and insertion torque (IT). Material and Mehods: A total of 47 implants divided in two groups: Test group (TI): 22 Tapered MIS® Seven implants; Control group (CI): 25 cylindrical Astra® Osseospeed implants. All implants were inserted following the manufacturers’ standard protocols. Implant primary stability was measured at the moment of implant placement by registering insertion torque values (ITv) and ISQ values by means of Osstell.
Comparison of the Primary and Secondary Stability of Implants with Anodized Surfaces and Implants Treated by Acids: A Split-Mouth Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
Pimentel Lopes de Oliveira GJ, Leite FC, Pontes AE, Sakakura CE, Junior EM
Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2016 Jan-Feb;31(1):186-90. doi: 10.11607/jomi.4212
PURPOSE:
The objective of this randomized controlled clinical split-mouth trial was to compare anodized implant surfaces and implant surfaces modified by acid etching in terms of primary and secondary stability.
CONCLUSION:
The different surfaces were similar in terms of primary and secondary stability of implants placed in the posterior mandible.
Multicentre prospective evaluation of implant-assisted mandibular removable partial dentures: surgical and prosthodontic outcomes
Payne AG, Tawse-Smith A, Wismeijer D, De Silva RK, Ma S
Clin Oral Implants Res. 2016 Jan 22. doi: 10.1111/clr.12769
OBJECTIVE:
To determine implant survival and prosthodontic maintenance of implant-assisted mandibular removable partial dentures in a multicentre prospective study up to 10 years.
CONCLUSION:
This clinical multicentre research complements previous case reports, case series, retrospective and prospective studies on the notion of implant-assisted removable partial dentures for partially edentulous patients. Late implant failures and increased prosthodontic maintenance when an attachment system is used identify the need for further research, including more robust statistical analyses.
The effect of hydrothermal spark discharge anodization in the early integration of implants in sheep sinuses
Duncan WJ, Gay JH, Lee MH, Bae TS, Lee SJ, Loch C.
Clin Oral Implants Res. 2016 Jan 22. doi: 10.1111/clr.12741
OBJECTIVES:
Spark discharge anodic oxidation forms a porous oxide film on titanium implant surfaces, which may increase surface roughness and enhance early osseointegration. This study aimed to clinically and histomorphometric compare commercially-available sandblasted (RBM) implants, treated with hydrothermal anodization and placed into an animal maxillary sinus model.
DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSIONS:
Early integration of RBM implants placed into thin maxillary sinus walls was not enhanced by hydrothermal anodization of implant surfaces. This may be related to the initial low stability of the implants and the relatively short healing period. However, non-anodized RBM surfaces showed promising results, with % BIC values comparable to the best estimates of other studies using sinus grafting. Whether the modification of the implant surfaces through anodization with simultaneous sinus grafting would promote enhanced early osseointegration, is a subject of future research.
Effects of platelet-rich plasma in association with bone grafts in maxillary sinus augmentation: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Lemos CA, Mello CC, Dos Santos DM, Verri FR, Goiato MC, Pellizzer EP.
Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2016 Jan 6. pii: S0901-5027(15)00271-4. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2015.07.012
Peri-implant bone loss clinical and radiographic evaluation around rough neck and microthread implants: a 5-year study
Calvo-Guirado JL, López-López PJ, Pérez-Albacete Martínez C, Javed F, Granero-Marín JM, Maté Sánchez de Val JE, Ramírez Fernández MP
Clin Oral Implants Res. 2016 Jan 7. doi: 10.1111/clr.12775
OBJECTIVE:
To evaluate marginal bone loss over 5 years around microthreaded implants placed in the maxillary anterior/esthetic zone and immediate restored with non-occlusal loading.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results of this study showed limited implant crestal bone loss 0.90 mm ± 0.26 mm and 100% of implant survival rate at 5-year follow-up of immediate restored implants with rough surface neck and microthreads.
Stability of simultaneously placed dental implants with autologous bone grafts harvested from the iliac crest or intraoral jaw bone
Kang YH, Kim HM, Byun JH, Kim UK, Sung IY, Cho YC, Park BW.
BMC Oral Health. 2015 Dec 30;15(1):172. doi: 10.1186/s12903-015-0156-x
BACKGROUND:
Jaw bone and iliac bone are the most frequently used autologous bone sources for dental implant placement in patients with atrophic alveolar ridges. However, the comparative long-term stability of these two autologous bone grafts have not yet been investigated. The aim of this study was to compare the stability of simultaneously placed dental implants with autologous bone grafts harvested from either the iliac crest or the intraoral jaw bone for severely atrophic alveolar ridges.
CONCLUSIONS:
These findings demonstrate that simultaneous dental implantation with the autologous intraoral jaw bone graft method may be reliable for the reconstruction of edentulous atrophic alveolar ridges.
Six-Year Radiographic, Clinical, and Soft Tissue Outcomes of Immediately Loaded, Straight-Walled, Platform-Switched, Titanium-Alloy Implants with Nanosurface Topography
Glibert M, De Bruyn H, Östman PO.
Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2016 Jan-Feb;31(1):167-71. doi: 10.11607/jomi.4162
PURPOSE:
This prospective, longitudinal study evaluated the survival, marginal bone levels, and soft tissue conditions for immediately loaded, straight-walled, platform-switched, titanium-alloy implants with an internal connection and nanosurface topography.
CONCLUSION:
This study based on 40 patients treated with 112 straight-walled, platform-switched, titanium-alloy implants with nanosurface topography yielded a 99.1% survival rate after a mean follow-up time of 6.2 years. Additionally, mean crestal bone loss was limited to 0.26 mm (SD = 0.38) after 1 year and 0.35 mm (SD = 0.45) after 6 years. Peri-implant infection associated with excessive bone loss above 2 mm was only encountered in one implant, and residual cement was shown to be responsible.
Influence of preservation of the alveolar ridge on delayed implants after extraction of teeth with different defects in the buccal bone
Pang C, Ding Y, Hu K, Zhou H, Qin R, Hou R.
Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015 Dec 16. pii: S0266-4356(15)00712-3. doi: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2015.11.025
Abstract
Our aim was to evaluate the influence of preservation of the alveolar ridge on delayed implants with different defects in the buccal bone. We enrolled 60 patients who had one posterior mandibular tooth extracted. Cone-beam computed tomography (CT) was used to measure the buccal bone defects in the alveolar ridge before the tooth was extracted (level A=3 to 5mm, and level B=more than 5mm). After the tooth had been extracted, the socket either had the alveolar ridge preserved (trial group) or it was left to heal spontaneously (control group). The changes in the dimensions of the alveolar ridge from preoperatively to 6 months postoperatively were evaluated by cone-beam CT. Suitable implants were inserted 6 months later, and their length and diameter recorded. The implant stability quotient was evaluated for the following 3 months. The dimensions of the bone in the alveolar ridge in the trial group were significantly less than those in the control groups in both levels. Fifty-seven patients required implants (except 3 in level B in the control group). There were more longer and wider implants in the trial group than in the control group in Level B. 3 months after implantation, there were no significant differences in implant stability quotients between the groups, though in the control group, Level B, the mean (SD) value was 69.50 (1.00) while in the other groups values were all above 70 at 3 months. We conclude that when the defect in the buccal bone was more than 5mm, the alveolar ridge preservation demonstrated a remarkable effect in preserving the alveolar ridge dimension and delayed implantation.
The Effects of Defect Type and Depth, and Measurement Direction on the Implant Stability Quotient Value
Shin SY, Shin SI, Kye SB, Hong J, Paeng JY, Chang SW, Yang SM.
J Oral Implantol. 2015 Dec;41(6):652-6. doi: 10.1563/AAID-JOI-D-13-0031
ABSTRACT
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of defect type and depth as well as measurement direction on implant stability in an ex vivo peri-implant bovine rib bone model. Six kinds of defects (3-wall 2.5 mm, 3-wall 5 mm, 1-wall 2.5 mm, 1-wall 5 mm, circumferential 2.5 mm, circumferential 5 mm), and control (no defect) were prepared in 14 bovine rib bones. A total of 84 defects and 14 controls were created. The same type and size of implants (4 × 10 mm) were placed in each group. The thickness of cortical bone and the insertion torque were measured for each defect, and the implant stability quotient (ISQ) value was measured 3 times from 4 different directions. The thickness of cortical bone ranged from 2.71-3.18 mm. Insertion torque decreased as the defect size increased. As the defect size for the same defect depth increased, the ISQ value decreased (P < .001). There were significant differences between the ISQ values obtained with different measurement directions only between the control and 3-wall 5 mm defect (P < .0001). The ISQ value opposite to the defect direction was higher than that in the defect direction in all 3 directions of the 3-wall and 1-wall 5 mm defects. ISQ values were influenced by defect type and depth. Loss of cortical bone reduced the stability of implants and reduced the ISQ value. Measurement direction also influenced ISQ values.
Photobiomodulation on dental implant osseointegration: Removal torque and resonance frequency analysis in rabbits
Blay A, Blay CC, Tunchel S, Gehrke SA, Shibli JA, Groth EB, Zezell DM
J Oral Implantol. 2015 Dec 11
ABSTRACT
The objective of this study was to investigate the effect of a low intensity laser on the stability and reverse torque resistance of dental implants installed in the tibia of rabbits. Thirty rabbits received 60 dental implants with the same design and surface treatment, one in each proximal metaphysis of the tibia. Three groups were prepared (n = 10 animals): conventional osseointegration without treatment (Con group); surgical sites irradiated with a laser beam emitted in the visible range 680 nm (Lg1 group); surgical sites irradiated with a laser beam with a wavelength in the infrared range – 830 nm (Lg2 group). Ten irradiation sessions were performed 48 h apart; the first session was during the immediate post-operation period. Irradiation energy density was 4 J/cm2 per point in two points on each side of the tibias. The resonance frequency and removal torque values were measured at two time points after the implantations (three and six weeks). Both laser groups (Lg1 and Lg2) presented a significant difference between RFA values at the baseline and the values obtained after three and six weeks (p>0.05). Although the removal torque values of all groups increased after six weeks (p<0.05), both laser groups presented greater mean values than those of the control group (p<0.01). Photobiomodulation using laser irradiation with wavelengths of 680 and 830 nm had a better degree of bone integration than the Con group after six weeks of observation time.
Influence of Implant Surfaces on Osseointegration: A Histomorphometric and Implant Stability Study in Rabbits
Soares PB, Moura CC, Claudino M, Carvalho VF, Rocha FS, Zanetta-Barbosa D.
Braz Dent J. 2015 Oct;26(5):451-7. doi: 10.1590/0103-6440201300411
ABSTRACT
The aim of this study was to evaluate the stability and osseointegration of implant with different wettability using resonance frequency analysis (RFA) and histomorphometric analysis (bone implant contact, BIC; and bone area fraction occupied, BAFO) after 2 and 4 weeks in rabbit tibiae. Thirty-two Morse taper implants (length 7 mm, diameter 3.5 mm) were divided according to surface characteristics (n=8): Neo, sandblasted and dual acid-etched; and Aq, sandblasted followed by dual acid-etched and maintained in an isotonic solution of 0.9% sodium chloride. Sixteen New Zealand rabbits were used. Two implants of each group were installed in the right and left tibiae according to the experimental periods. The RFA (Ostell(r)) was obtained immediately and after the sacrifice (2 and 4 weeks). The bone/implant blocks were processed for histomorphometric analysis. Data were analyzed using two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test and Pearson’s correlation for ISQ, BIC and BAFO parameters (p=0.05). No significant effect of implant, period of evaluation or interaction between implant and period of evaluation was found for BIC and BAFO values (p>0.05). Only period of evaluation had significant effect for RFA values at 4 weeks (p=0.001), and at 2 weeks (p<0.001). RFA values were significantly higher at the final period of evaluation compared with those obtained at early periods. There was a significant correlation between BIC values and BAFO values (p=0.009). Both implant surfaces, Aq and Neo, were able to produce similar implant bone integration when normal cortical bone instrumentation was performed.
Locators versus magnetic attachment effect on peri-implant tissue health of immediate loaded two implants retaining a mandibular overdenture: a 1-year randomised trial
Elsyad MA, Mahanna FF, Elshahat MA, Elshoukouki AH
J Oral Rehabil. 2015 Nov 9. doi: 10.1111/joor.12368
ABSTRACT
This study aimed to evaluate peri-implant tissue health of immediate loaded two implants retaining a mandibular overdenture with either magnetic or locator attachment. Thirty two completely edentulous patients (20 males/12 females) were randomly assigned into two groups. Each patient received two implants in the canine area of the mandible using flapless surgical technique. Mandibular overdentures were immediately connected to the implants with either magnetic (group I, GI) or locator (group II, GII) attachments. Peri-implant tissue health was evaluated clinically in terms of plaque scores (PI), bleeding scores (BI), probing depth (PD), implant stability (ISQ) and interleukin-1-β (IL-1b) concentrations in peri-implant sulcular fluid. PI, BI and PD were measured at mesial, distal, buccal and lingual surfaces of each implant. Radiographic evaluation was performed in terms of vertical (VBL) and horizontal (HBLO) alveolar bone loss. Evaluations were performed 2 weeks (T0), 6 months (T1) and 12 months (T2) after overdenture insertion. Plague scores, PD, IL-1b, VBL and HBLO increased significantly with time. ISQ decreased significantly with time. BI showed no significant differences between observation times. GI recorded significant higher PI, ISQ and IL-1b at T2 compared to GII. GII recorded significant higher VBL than GI at T2 only. For HBLO, no significant differences between groups were noted. VBL and HBLO showed a significant positive correlation with PD. Locator attachments for immediate loaded implants retaining mandibular overdentures are associated with decreased plaque accumulation, decreased implant stability, decreased interleukin-1β concentration in peri-implant cervicular fluid and increased per-implant vertical bone loss compared to magnetic attachments after 1 year.