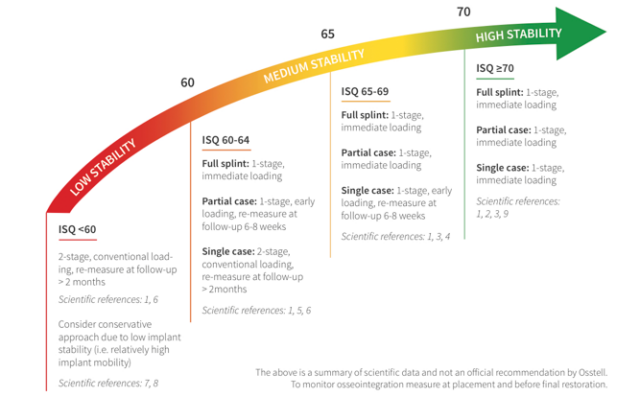
The Osstell ISQ Scale
Osstell’s patented technology uses Resonance Frequency Analysis (RFA) that measures the frequency with which a device vibrates. By comparing resonance frequencies, the stability of a dental implant can be determined as the resonance frequency changes with different stabilities.
Read the full article
The Technique Behind Osstell
Osstell’s patented technology uses Resonance Frequency Analysis (RFA) that measures the frequency with which a device vibrates. By comparing resonance frequencies, the stability of a dental implant can be determined as the resonance frequency changes with different stabilities.
Read the full article
How ISQ Correlates to Torque
Torque is sometimes used to describe the stability of an implant. However, torque does not necessarily correlate to implant stability. Torque measures the rotational friction between the implant and the bone combined with the force required to cut the bone if that is the case, and the pressure force from the surrounding bone.
Read the full article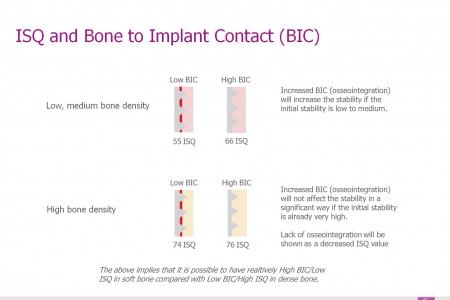
How ISQ correlates to BIC
BIC, or Bone to Implant Contact, is the percentage of the implant surface in contact with bone on a microscopic level.
Read the full article