Sign up to our newsletter to receive news, videos and more clinical cases like this
Current status in OsstellConnect:
Patient records
Implant treatments
ISQ Measurements
Current status in OsstellConnect:
Patient records
Implant treatments
ISQ Measurements
Current status in OsstellConnect:
Patient records
Implant treatments
ISQ Measurements
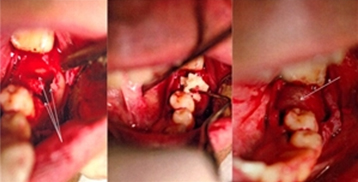
Clinical case by Dr M Almasri, Dr A-J Camarda, Dr H Ciaburro, Dr F Chouikh, and Dr S-J Dorismond. Three patients who had undergone a mandibular posterior dental extraction with subsequent buccal bone plate compromise.
Dr M Almasri McGill University Dr A-J Camarda, Dr H Ciaburro, Dr F Chouikh, Dr S-J Dorismond Canada and Université de Montréal, Canada
Three patients who had undergone a mandibular posterior dental extraction with subsequent buccal bone plate compromise.
Immediate alveolar bone reconstruction was performed using a Demineralized Bone Matrix allograft mixed with a Calcium Sulfate graft binder. Implants and healing abutments were placed after 6, 9 and 12 months, followed with crown placement at 3, 5 and 5 months later, respectively.
Securing appropriate stability and osseointegration at the time of healing.
Implants and healing abutments were placed after 6, 9 and 12 months, followed with crown placement at 3, 5 and 5 months later, respectively. Periodic clinical and radiographic re-evaluation of the implants occurred at between 10 and 39 months of function. Osstell (ISQ) Mentor® was used to objectively evaluate the long term biological and functional stability of the implants. ISQ at last visit ranged from 87 to 90, indicating high stability.
The clinician may now objectively assign each implant a numerical value, representing its mechanical stability at placement and its biological, long term stability at implant re-evaluation, with the introduction of the Ostell ISQ Mentor ® device (Osstell AB, Sweden)4. Interpretation is based on the numeric implant-bone Interface Stability Quotient (ISQ) value. Thus, a successful, biologically osseointegrated implant has an ISQ value of, ideally, greater than 65 while an ISQ value of less than 50 indicates increased risk of implant failure.
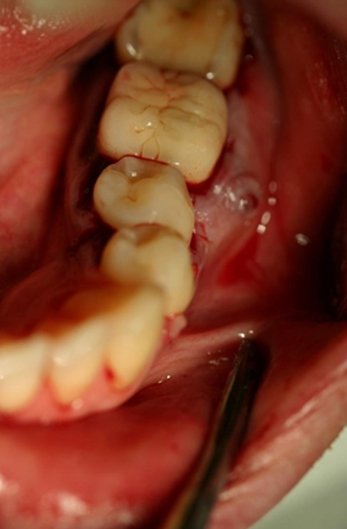
Figure 1: Patient 3. Preoperative view of tooth no. 3.6 with chronic fistulous area at the buccal bifurcation.

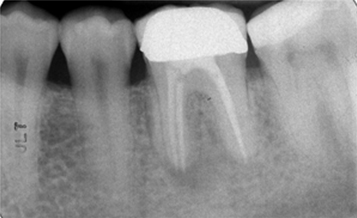
Figure 2: Patient 3. Preoperative periapical radiograph of tooth no. 3.6. Note the radiolucency at the bifurcation and mesial root areas.