L’échelle ISQ
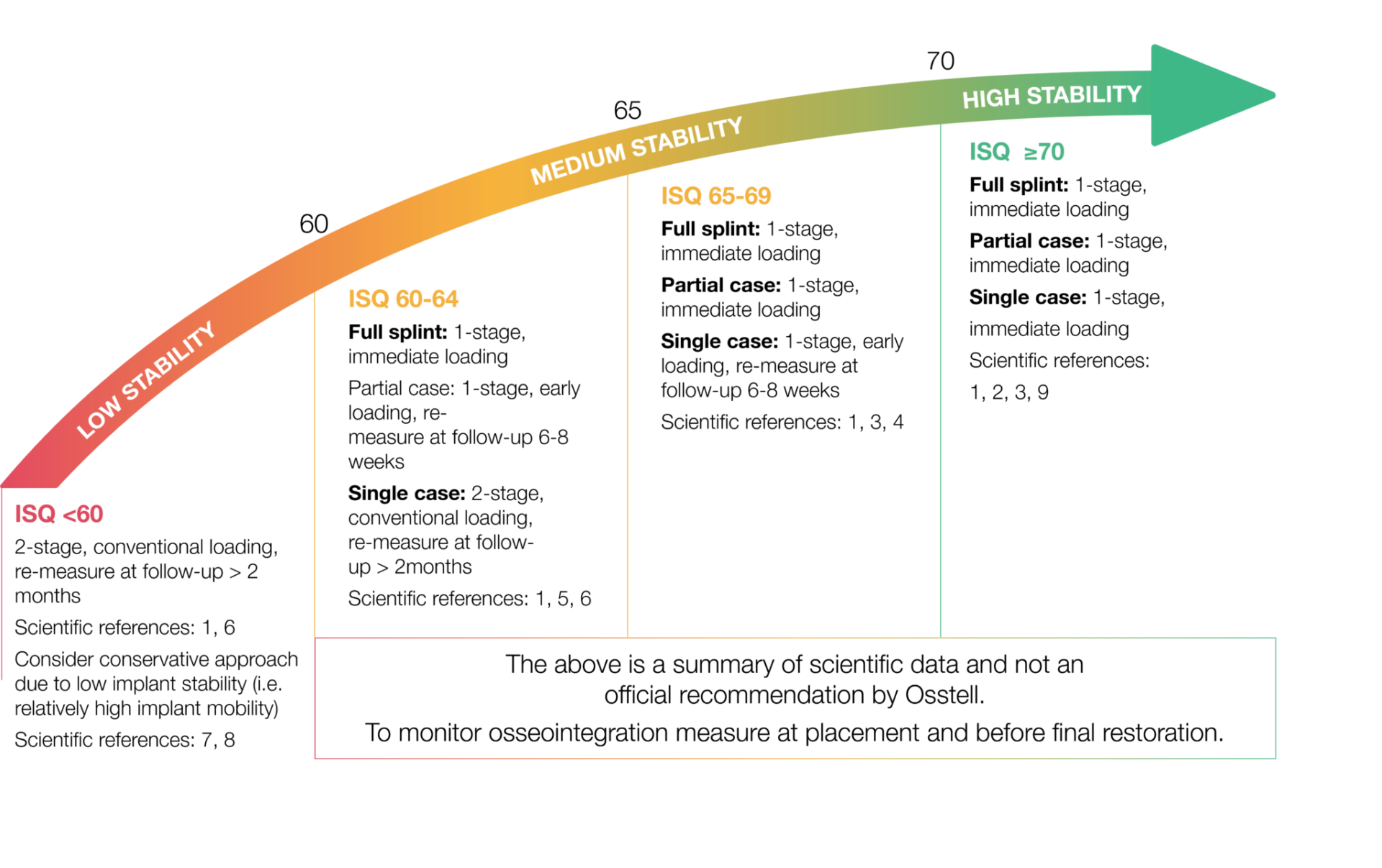
L'ISQ, ou Implant Stability Quotient (quotient de stabilité de l'implant), est une échelle de 1 à 99. Il mesure la stabilité d'un implant. L'échelle ISQ a une corrélation non linéaire par rapport à la micromobilité. Avec plus de 1500 références scientifiques, nous savons maintenant qu'une stabilité est élevée au-delà d'un ISQ de 70, qu'elle est modérée entre 60 et 69 et considérée comme faible en dessous de 60.
L’ISQ, ou Implant Stability Quotient (quotient de stabilité de l’implant), est une échelle de 1 à 99. Il mesure la stabilité d’un implant. L’échelle ISQ a une corrélation non linéaire par rapport à la micromobilité. Avec plus de 1500 références scientifiques, nous savons maintenant qu’une stabilité est élevée au-delà d’un ISQ de 70, qu’elle est modérée entre 60 et 69 et considérée comme faible en dessous de 60.
Le quotient de stabilité de l’implant (ISQ) est un standard mondial objectif pour mesurer la stabilité de l’implant. La plage clinique de l’ISQ est normalement comprise entre 55 et 80. Des valeurs supérieures sont généralement observées dans la mandibule plutôt que dans le maxillaire. L’échelle ISQ a une corrélation non linéaire par rapport à la micromobilité. Avec plus de 1500 références scientifiques, nous savons maintenant qu’une stabilité est élevée au-delà d’un ISQ de 70, qu’elle est modérée entre 60 et 69 et considérée comme faible en dessous de 60. Si la valeur ISQ initiale est élevée, une légère chute de stabilité est normalement compensée avec le temps. Une chute ou diminution importante de stabilité doit être considérée comme un signe alarmant. Il est attendu que des valeurs inférieures soient plus élevées à l’issue de la période de cicatrisation. Le constat inverse pourrait être un signe d’échec implantaire et des mesures devraient être envisagées.
Références
1. 20 Jahre Erfahrung mit der Resonanzfrequenzanalyse
Sennerby L Prof, Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg, Sweden Implantologie 2013;21(1):21-33 (In German) Translated from German “It is likely that ISQ measurements can be used as one additional parameter for diagnosis of implant stability and decision-making during implant treatment and follow-up. The threshold values are the present author’s own somewhat conservative suggestions based on own experience and other values may be relevant for other clinicians and implant designs. The green zone contains “safe” implants showing primary ISQ values from, for instance 70 and above. The red zone contains “questionable” implants with an ISQ value below for instance 55. The yellow zone represents implants with an ISQ from 55 to 70”.
2. Immediate vs. early loading of SLA implants in the posterior mandible: 5-year results of randomized controlled clinical trial.
Kokovic V, Jung R, Feloutzis A, Todorovic V, Jurisic M, Hämmerle C Clinical Oral Implants Research, 00, 2013, 1-6 After 5 years, survival in the both groups was 100 %. The mean value of primary implant stability was 76,92 ± 0,79 ISQ. In the first 6 weeks, ISQ values significantly increased in the test group as well as in the control group. Based on these results, the self-tapping implants inserted in posterior mandible can provide adequate primary stability value as the main factor for immediate and early loading protocol.
3. Early Loading of Nonsubmerged Titanium Implants with a Chemically Modified Sand-Blasted and Acid-Etched Surface: 6-Month Results of a Prospective Case Series Study in the Posterior Mandible Focusing on Peri-Implant Crestal Bone Changes and Implant Stability Quotient (ISQ) Values
Michael M. Bornstein, Dr. med. dent.; Christopher N. Hart, DMD; Sandro A. Halbritter, Dr. med. dent.; Dean Morton, BDS, MS;† Daniel Buser, Prof. Dr. med. dent. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2009 If the ISQ value at day to load is < 65, an additional healing period is recommended, and the ISQ values is measured again 3 weeks later until the required level is reached. This approach is practical and well understood by patients. (Prof. Daniel Buser prefers ≥ 70 ISQ, single teeth, early loading/Straumann, otherwise add three weeks, according to an oral presentation given at the Osstell Scientific Symposium in connection to the of the EAO 2010.)
4. The Predictive Value of Resonance Frequency Analysis in the Surgical Placement and Loading of Endosseus Implants
Serge Baltayan, Joan Pi-Anfruns, Tara Aghaloo, Peter Moy J Oral Maxillofac Surg 74:1145-1152, 2016 One-stage placement of implants with ISQ values greater than 66 can be performed. Implants with ISQ values less than or equal to 66 should be placed using the two-stage protocol, which shows a higher survival rate. The computed ISQ = 66 cut-off value used to select between one-stage and two-stage placement is validated in this study. Moreover, early loading of implants with ISQ values greater than 64 can be performed. Implants with ISQ values less than 64 should utilize traditional loading, which shows a higher survival rate. The computed ISQ = 64 cut-off value used to select between early and traditional loading is validated in this study. Higher ISQ values at osseointegration correlate with higher survival rates.
5. Direct Loading of Implants
Pär-Olov Östman DDS, PhD, MD, Private practitioner, Falun- and Biomaterial group, Sahlgrenska Academy, Gothenburg – Tandläkartidningen årg 100 nr 3, 2008 Paper IV 20 consecutive patients with totally edentulous maxillas were included in the study. The criteria for direct loading was insertion torque 30 Ncm and an ISQ > 60 on the most posterior implants and a sum of 200 ISQ (average 50 ISQ) on the 4 anterior implants. The overall conclusion with the thesis is that dental implants can be direct loaded with a good result if high primary stability can be obtained and if a stable provisional bridge with good occlusion is splinting the implants.
6. Diagnosis of Implant Stability and its Impact on Implant Survival: A Prospective Case Series Study
Daniel Rodrigo, Luis Aracil, Conchita Martin, Mariano Sanz Clin. Oral Impl. Res. 21, 2010; 255-261 The evaluation of RFA values to assess implant secondary stability (Osstell 2) demonstrated a statistically significant correlation with implant outcome. In fact, no implant with ISQ > 60 failed, while 19 % of implants with ISQ < 60 failed.
7. The relationship between resonance frequency analysis (RFA) and lateral displacement of dental implants: An in vitro study
Pagliani L, Sennerby L, Petersson A, Verrocchi D, Volpe S & Andersson P Journal of Oral Rehabilitation 2012 Both RFA and displacement measurements correlated with bone density. It is concluded that RFA measurements reflect the micromobility of dental implants, which in turn is determined by the bone density at the implant site. The correlation between ISQ and micron was non-linear and micro motion was reduced with app. 50 % from 60 ISQ to 70 ISQ.
8. Implant Stability Quotient (ISQ) vs Direct in Vitro Measurement of Primary Stability (Micromotion): Effect of Bone Density and Insertion Torque
Paolo Trisi PhD, Teocrito Carlesi DDS, Marco Colagiovanni DDS, Giorgio Perfetti MD, DDS Journal of Osteology and Biomaterials, Volume 1, Number 3, 2010 Results showed a high dependence between the observed micromotion and the ISQ values, indicating that micromotion decreased with increasing ISQ values. An in vitro study and the results cannot be directly transferred to clinical applications.
9. Early loading of titanium dental implants with an intra-operatively conditioned hydrophilic implant surface after 21 days of healing.
Stefan Paul Hicklin, Esther Schneebeli, Vivianne Chappuis, Simone Francesco Marco Janner, Daniel Buser, Urs Brägger Clin. Oral Impl. Res 00, 2015; 1-9 Functional occlusal loading of implants with a hydrophilic, moderately rough endosseal surface and ISQ values > 70 three weeks after placement, appears to be a safe and predictable treatment option in healed sites in the posterior mandible without need of bone augmentation procedures.

